
Media Drive For Mac
Chromecast to mac for free. To broadcast audio or video wirelessly from your Mac to the big screen (TV), you will need a Google Chromecast, a Television or projector, Chrome web browser (free for Mac), a WiFi network, and of course a Mac computer.
Looking to share an external hard drive between a Mac and PC? The best way to do it is with a drive formatted as FAT32. Though this format has some limitations, it enjoys nearly universal support from active platforms, including Mac and Windows operating systems, and many gaming and Linux OSs. The chief drawbacks of FAT32 involve file and partition size limitations. FAT32 imposes a size limit of 4GB on single files.
So if you work with bulky video clips, for example, adopting FAT32 may not be a good idea. When formatting partitions, Windows 7's Disk Management utility won't let you create one that's larger than 32GB, whereas Mac OS X Lion can create partitions as large as 2TB using its Disk Utility application. Finally, Mac OS X's Time Machine backup utility won't work with FAT32.
To format a drive as FAT32 from a Mac, follow these simple steps. [ Further reading: Best NAS boxes for media streaming and backup ] 1. Set up your drive following the manufacturer's instructions.
Windows prefers to use NTFS (which stands for New Technology File System, though it has been around for nearly 20 years now). Macs running Snow Leopard or Lion can read from drives formatted as NTFS, but they can't write to such drives unless you install a third-party driver or muck about in the Terminal. Conversely, Windows 7 can't read and write to drives formatted as HFS+--also known as Mac OS Extended (journaled)--unless you install third-party software. Create a bootable drive usb mac for sierra vista. Formatting From a Mac To format a drive as FAT32 from a Mac, follow these simple steps. Set up your drive following the manufacturer's instructions. Connect the power supply (if necessary), connect to the Mac via USB or FireWire, and turn on the drive.
The drive should automatically mount on your Mac's desktop (if the finder preferences are set to show external drives). If the drive is not formatted, you may get a message saying that the drive is unreadable by Mac OS X and asking you whether you want to format it via Disk Utility. We're going to do this anyway, so open Disk Utility from the prompt or by navigating to /Applications/Utilities. Select MS-DOS (FAT) as the format. Mac OS X won't let you create a FAT32 partition larger than 2TB; so if your drive is larger than that, you'll need to divide the available drive capacity into multiple partitions. You can format the remaining space as a second FAT32 partition or as an HFS+ partition, or you can leave it as unallocated space. To create a new partition, click the drive in the list on the left side of the Disk Utility menu.
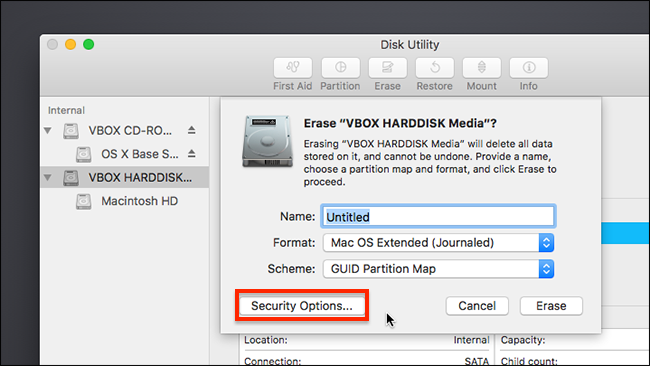
Click the Partition button in Disk Utility's main window. By default, Mac OS X will use the GUID partition table to format the drive. You can use this and still share FAT32 volumes with a PC, but if you'll primarily be using the drive with Windows, and if the full capacity of the drive doesn't exceed 2TB, the wiser course is to wipe the drive and then use Windows' Master Boot Record (MBR) partition scheme.